Occurred in lowincome countries Similarly, healthy life 1 See section 2 expectancy rose by 18% in lowincome countries compared with 8% globally over the same period (1) The recent life expectancy gains in lowincome countries are largely due to major reductions in mortality in children under 5 years in lowincome countries (1), a reduction The life expectancy jumped from 509 years in 12, to 538 years in 15, according to the report Deaths resulting from the 10 biggest health risks in Africa – such as lower respiratory infections, HIV and diarrhoeal diseases – dropped by half between 00 and 15, partly as a result of specialised health programmesMany factors can explain these lower gains in life expectancy, including 1) the highly fragmented nature of the US health system, with relatively few resources devoted to public health and primary care, and a large share of the population uninsured;
D Nb Info
Low life expectancy in africa can be partly attributed to the ravages of aids
Low life expectancy in africa can be partly attributed to the ravages of aids-A combination of factors, including AIDS, keeps life expectancy low in many parts of Africa In the United States, the 1900s were marked by a rather low life expectancy About half of all children born in 1900 were only expected to live to reach the age of 50Life expectancy is low This may be due to lack of clean drinking water, proximity to the hospital or health care center, etc Some less developed countries, life expectancy at birth may be lower than life expectancy at age 1, because of high infant mortality rates commonly due to lack of access to a clean water supply or infectious disease To



1
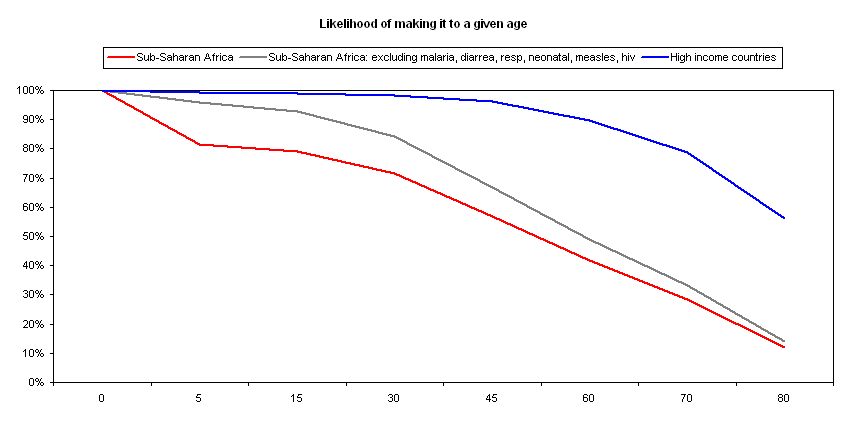
84 Journal of African Development (15) 17–114 USD with aid to prevent and manage HIV/AIDS seeing a 35 fold increase2 Figures 1a–1c show the flow of DAH, source of DAH, and DAH to focus areas to developing countries over the 1990–12 period Regardless of how it is measured, there is clear evidence that the flow In 1960, life expectancy in the region hovered at 40 Now, individuals can expect to reach an average of 59 years of age This sharp incline in life expectancy of lowincome countries is attributed to a greater access to aid programs and organizations than ever beforeLife expectancy Using the the mortality rates on which the above differences are based, we constructed the chart below, which shows the the probability that a child born in subSaharan Africa reaches a given age We also show life expectancies for subSaharan Africa excluding the major causes of childhood mortality (under5 deaths from malaria
Improving the quality of life in SA An increased number of tourists travelling to South Africa, higher life expectancy and more children attending childhood development facilities These are some of the highlights that the country experienced between 1994 and 14 This is according to the 14 Development Indicators Report, which was released Our research shows that the average life expectancy for men in subSaharan Africa is 62 years For women it's 66 years People live longer in Africa, but rich diseases hurt progress —Conversely, improvement in health conditions of people can be also attributed to economic development Thus, higher levels of developments results in improved nutrition and sanitation, advances in medical knowledge and technologies that reduces mortality among the population there by increasing their life expectancy at birth or at specific age
A High Standard of Living, Brought Low by AIDS in South Africa In 1994 South Africa's regime of apartheid, under which the black majority was suppressed and discriminated against by the white minority, came to an end 1 The African National Congress (ANC) won the first free elections in the same year, and the paty has held power ever since Changes in life expectancy can be used to track the impact of populationwide health threats, such as the HIV epidemic in subSaharan Africa TheAfrica's Underdevelopment An Issue of External Influence Iwok, U M and low life expectancy among others multinationals and resistance to military aids and assistance among others can go a long way in repositioning Africa's pride of place in the global habitat




Mass Hiv Treatment And Sex Disparities In Life Expectancy Demographic Surveillance In Rural South Africa




Pdf Socio Economic Determinants Of Life Expectancy In Sub Saharan
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an average Nigerian is expected to live approximately 552 years from birth6 This life expectancy is the sixth lowest in the world It is also significantly below the global average of 72 years and Africa's average of 612 yearsChart and table of Africa life expectancy from 1950 to 21 United Nations projections are also included through the year 2100 The current life expectancy for Africa in 21 is 6353 years, a 046% increase from ; Introduction The surge in life expectancy in the African region since 00 is evidently the greatest since the reverse gains in the 1990s Life expectancy at birth increased in the region by 94 years to 60 years, with some countries experiencing as high as 42% rise between 00 and 14 These remarkable gains have taken place mainly in the context of increased



Un Org



D Nb Info
Life expectancy is the average number of years a person in a population could expect to live after age x It is the life table parameter most commonly used to compare the survival experience of populations The age most often selected to make comparisons is 00 (ie, birth), although, for many substantive and policy analyses, other ages such South Africa's Aids programme has been hailed as a model for HIV treatment Life expectancy in South Africa has increased dramatically over the last decade, mainly thanks to lifesaving Aids drugsHowever, in recent years the life expectancy in Africa has fortunately been on the rise Since 00, the average life expectancy in African countries has increased from percent to 42 percent That is the biggest increase in life expectancy recorded in that time frame in all



Seejph Com




Infographic Life Expectancy In South Africa From 1960 To 15 South Africa Gateway
2) healthrelated behaviours, including greater obesity rates, higher consumption of prescription and illegal drugs, more deaths from roadLife expectancy Years of life lost SAMRC BURDEN OF DISEASE RESEARCH UNIT Data cleaning, HIV/AIDS is usually in Group I, however, in leading to death and a consequence of diseases entered on lower lines of Part 1 This is also known as the terminal, direct or final cause of death Africans are living longer than at any point in the last 25 years Plenty to smile about Published This article is more than 2 years




Health And Disease In Southern Africa A Comparative And Vulnerability Perspective Sciencedirect




Estimating Trends In Life Expectancy In Hiv Positive Individuals The Lancet Global Health
Factors, Malaria the Most Common Disease Affecting Pregnant Women in Africa Nigeria and Cameroon Glob J Reprod Med 18; The average life expectancy across the whole continent was 61 years for males and 65 years for females The average life expectancyRates decreased in these countries by 675%, 654%, 636%, and 618% respectively Causes of Death One of the major causes of underfive mortality is neonatal sepsis In 10, 15% of newborn deaths in Africa can be attributed to infections related to the delivery process




Genocide By Denial How Profiteering From Hiv Aids Killed Millio Pdf Uganda Hiv Aids



Clinmedjournals Org
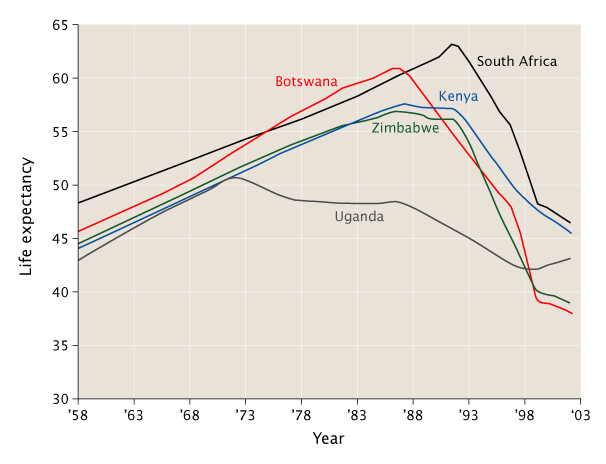
Life expectancy remains lowest in subSaharan Africa, where people can expect to live 53 years on average Six countries in this region have lower life expectancies today than they did in the 1970s Botswana, Lesotho, South Africa, Swaziland, Zambia, and Zimbabwe These countries also have some of the world's highest HIV prevalencesHow to cite this article İlker E, Akinleye A A, Meliz Y Life Expectancy; At the other end of the scale, the rankings reflect graphically the ravages of Aids in much of Africa All 10 lowest rated countries are in subSaharan Africa and healthy life expectancy in strife



1




Pdf Socio Economic Determinants Of Life Expectancy In Sub Saharan Africa Mohammed Abubakari Academia Edu
Human development in subSaharan Africa has stagnated while progress in other parts of the world has accelerated, widening the gap between the world's richest and poorest countries, warns this year's United Nations Human Development Index (HDI), which finds life expectancy in the region lower today than 30 years ago mainly because of the ravages of Implications of low life expectancy (1) Loss of productive workforce In many parts of African continent, life expectancy continued to decrease For instance, Botswana people use to live up to 60 years old but now averaging at 40 years of age South Africa which is relatively the performer among African peers, does not do so well too COVID19 has generated a huge mortality toll in the United States, with a disproportionate number of deaths occurring among the Black and Latino populations Measures of life expectancy quantify these disparities in an easily interpretable way We project that COVID19 will reduce US life expectancy in by 113 y Estimated reductions for the Black and Latino



Bioline International Official Site Site Up Dated Regularly




Health And Disease In Southern Africa A Comparative And Vulnerability Perspective Sciencedirect
Pulse Nigeria In 18, Nigeria had the lowest life expectancy in West Africa This was according to the World Health Organization (WHO)The life expectancy for Africa in 19 was 6295 years, a 046% increase According to the report, life expectancy at birth stands at 61 years, having increased from an estimated 52 years in 05 The rise in life expectancy can be attributed to two important trends first, the number of AIDS related deaths is estimated to have decreased from 363 910 deaths in 05 (51% of all deaths) to 171 733 deaths in 14 (31% of all deaths)



Ilo Org




Cepal Review No 133 By Publicaciones De La Cepal Naciones Unidas Issuu
Gain in life expectancy over the years For instance, in Rwanda the life expectancy has risen from a low of 267 years between 1992 – 1993 to 690 years in 19 The remarkable improvement in life expectancy recorded in Rwanda can be linked to, among other factors, the reforms and health initiatives being implemented by the governmentIn Africa, a high mortality of HIV/Aids bean (062 per cent) and Asia (061 per cent) In Africa, the increase in life expectancy at age 60 tancy at birth of the world can be attributed to Life expectancy in South Africa versus Africa South Africa's life expectancy is also lower than most African countries with The Congo being placed at 643 years, Malawi at 642 years, Kenya at 667 years and Rwanda at 68 years The only country that has a lower average life expectancy is Nigeria at 552 years



Ilo Org



Hdr Undp Org
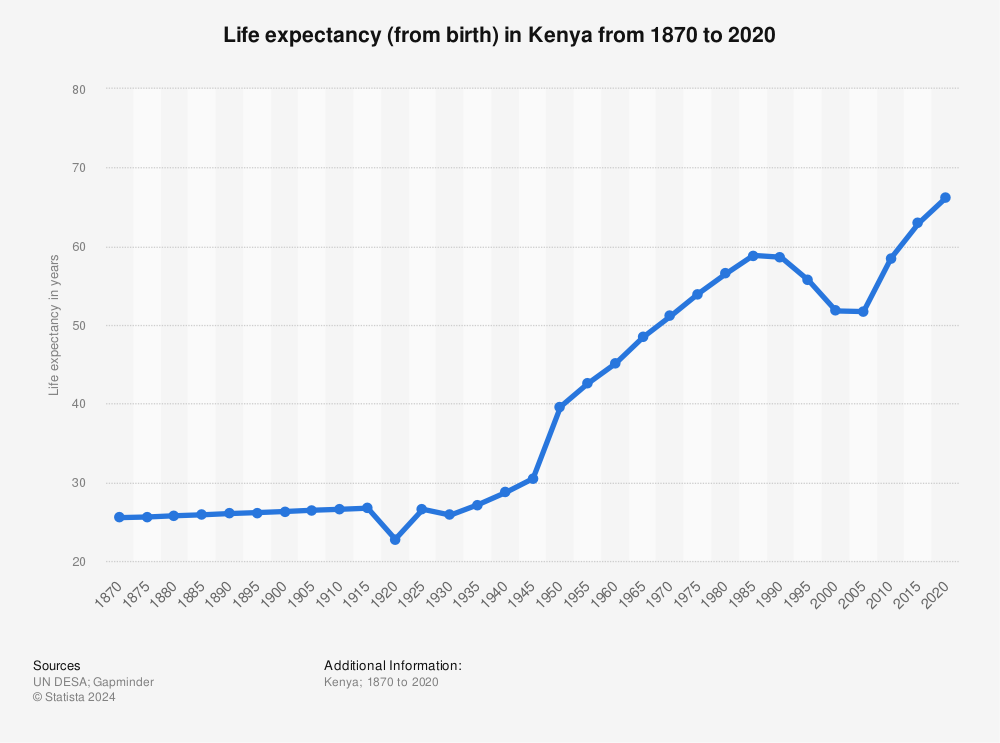
Africa is a continent that has long had a very low life expectancy;The life expectancy for Africa in was 6324 years, a 046% increase from 19; Life Expectancy in Africa Slowly Gaining on Developed World NAIROBI — The World Health Organization (WHO) reported in May 16 that the average life expectancy in Kenya has increased in the past 15 years, from 51 to 634 years This statistic shows the longterm impact of medical and social programs that support countries like Kenya



Battling Hiv Aids Cqr



Life Expectancy In Sub Saharan Africa Givewell
The countries with the lowest life expectancy worldwide include the Central African Republic, Chad, and Lesotho As of 19, people born in the Central African Republic could be expected to live LIFE EXPECTANCY Life expectancy (or the expectation of life) is the average length of life remaining to be lived by a population at a given age It is computed in the process of building a life table and can be computed for any age in the life table Life expectancy at birth is the most commonly presented value because this measure provides a succinct indicator of mortality thatLife expectancy at birth, total (years) SubSaharan Africa ( 1 ) United Nations Population Division World Population Prospects 19 Revision, or derived from male and female life expectancy at birth from sources such as ( 2 ) Census reports and other statistical publications from national statistical offices, ( 3 ) Eurostat Demographic




Health And Disease In Southern Africa A Comparative And Vulnerability Perspective Sciencedirect




Expedition Earth Population Graph With Or Without Aids Sub Saharan Africa
5(1) DOI /GJORM51 003 Global ournl Lifestyle diseases threaten lifespan in Africa The average life expectancy for men in subSaharan Africa is 62 years while for women, it's 66 years Net photo People in subSaharan Africa are now living longer than ever before A child born in the region today is expected to live up to 64 years on average This is a remarkable increase of A major problem facing the healthcare system is finance, and this is partly attributed to the Government of Ghana's (GoG) low fiscal capacity and commitment to health For example, the government spent 49% of its gross domestic product (GDP) on healthcare in 09 and increased it to 52% in 12



Unfccc Int



Hivpolicy Org



Portals Iucn Org




Life Expectancy In Africa



Cgdev Org




Africa Life Expectancy 1950 Statista




How Can We Support Widows In Africa World Economic Forum



Citeseerx Ist Psu Edu



Hivhealthclearinghouse Unesco Org




Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus And Obesity In Sub Saharan Africa Tuei 10 Diabetes Metabolism Research And Reviews Wiley Online Library



Emerald Com



Data Unicef Org




Infographic Life Expectancy In South Africa From 1960 To 15 South Africa Gateway




Supplemental Materials For The Path To Longer And Healthier Lives For All Africans By 30 The Lancet Commission On The Future Of Health In Sub Saharan Africa The Lancet



Apps Who Int



Jstor Org



Alzint Org




Health And Disease In Southern Africa A Comparative And Vulnerability Perspective Sciencedirect



Bioline International Official Site Site Up Dated Regularly



Kenya Life Expectancy 1870 Statista




Adult Mortality In The Cities Of Bulawayo And Harare Zimbabwe 1979 08 Dlodlo 11 Journal Of The International Aids Society Wiley Online Library



Afro Who Int



Apps Who Int



Who Int




How The Human Life Span Doubled In 100 Years The New York Times



Jstor Org




Health And Disease In Southern Africa A Comparative And Vulnerability Perspective Sciencedirect




Supplemental Materials For The Perfect Storm Incarceration And The High Risk Environment Perpetuating Transmission Of Hiv Hepatitis C Virus And Tuberculosis In Eastern Europe And Central Asia The Lancet



Swissre Com



Burden And Changes In Hiv Aids Morbidity And Mortality In Southern Africa Development Community Countries 1990 17 Bmc Public Health Full Text



Documents Worldbank Org




Sustainable Development In Latin America And The Caribbean By Publicaciones De La Cepal Naciones Unidas Issuu




Pdf Socio Economic Determinants Of Life Expectancy In Sub Saharan




References In Global Burden Of Disease In Young People Aged 10 24 Years A Systematic Analysis The Lancet



Afdb Org



Skin Hiv1 And Hiv2 Symptoms



Life Expectancy In Sub Saharan Africa Givewell



Un Org




Pdf Mortality Trends In The Era Of Antiretroviral Therapy Evidence From The Network For Analysing Longitudinal Population Based Hiv Aids Data On Africa Alpha



Un Org



1



Reliefweb Int




Guidebook Addressing Climate Change Challenges In Africa Unep



Afro Who Int




Adult Mortality In The Cities Of Bulawayo And Harare Zimbabwe 1979 08 Dlodlo 11 Journal Of The International Aids Society Wiley Online Library




Hiv Aids In The Caribbean And Central America Everycrsreport Com




Health And Economic Development Emerald Insight




Africa Human Development Report 12 By Undp Turkiye Issuu




Education And Hiv Aids In The Caribbean Unesco



1



Why Did Aids Not Affect People Until The 80 S Quora



Digitallibrary Un Org



Coursework Topic The Correlation Between Gdp Per Capita Against Life Expectancy At Birth In Different Countries Writework



Etheses Whiterose Ac Uk




Concealed Sufferings Social Responses To The Shared Secrets Manualzz




The Visual Economy Of Hiv Aids



Assets Publishing Service Gov Uk



c News Health Life Expectancy In Africa Plummets Due To Aids



Preventionweb Net



Pdf Socio Economic Determinants Of Life Expectancy In Sub Saharan



c News Africa Aids To Kill One In Two Africans




The Embodiment Of Inequality Aids As A Social Condition And The Historical Experience In South Africa Embo Reports Vol 4 No S1




Pdf Hiv Aids And Conflict In Africa Why Isn T It Even Worse



Kas De



Life Expectancies Of South African Adults Starting Antiretroviral Treatment Collaborative Analysis Of Cohort Studies



The Effect Of Interventions On The Transmission And Spread Of Hiv In South Africa A Phylodynamic Analysis Scientific Reports




Africa Life Expectancy 1950 Statista



c News Africa Life Expectancy Still Falling In Africa




Life Expectancy In Africa 19 Statista




Public Health And Population Health Understanding Health And Disease Springer Publishing




Pdf Socio Economic Determinants Of Life Expectancy In Sub Saharan



Hivhealthclearinghouse Unesco Org




Hiv Book Future Of Infected And Affected



Apps Who Int



Data Highlights 21 Troubling Health Trends Holding Back Progress On Life Expectancy Epi



Assaf Org Za



Battling Hiv Aids Cqr




Tool 3 Millennium Development Goals Iwrm




Pdf Mortality Trends In The Era Of Antiretroviral Therapy Evidence From The Network For Analysing Longitudinal Population Based Hiv Aids Data On Africa Alpha




The Embodiment Of Inequality Aids As A Social Condition And The Historical Experience In South Africa Embo Reports Vol 4 No S1




Health And Economic Development Emerald Insight



Apps Who Int



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿